FreeMat v4.2
Copyright (c) 2002-2008 by Samit Basu
Licensed under the GNU Public License (GPL)
Type <help license> to find out more
<helpwin> for online help
<pathtool> to set or change your path
Use <dbauto on/off> to control stop-on-error behavior
Use ctrl-b to stop execution of a function/script
JIT is enabled by default - use jitcontrol to change it
Use <rootpath gui> to set/change where the FreeMat toolbox is installed
--> Warning: unable to find function base to single step
--> Warning: Last warning repeats... suppressing more of these
--> loge(e)
Error: Undefined function or variable loge
--> e=
Error: Unexpected input
e=
^
--> sprt(4)
Error: Undefined function or variable sprt
--> sqrt(67)
ans =
8.1854
--> sqrt(4)
ans =
2
--> ln(2)
Error: Undefined function or variable ln
--> log(2.71)
ans =
0.9969
--> 2*sin(6.28)
ans =
-0.0064
--> 3=4
Error: Unexpected input
3=4
^
--> log(e)
ans =
1
--> e=
Error: Unexpected input
e=
^
--> e
ans =
2.7183
--> e=1.1
e =
1.1000
--> e
ans =
1.1000
--> e
ans =
1.1000
--> log(e)
ans =
0.0953
--> e=2.7183
e =
2.7183
--> pi
ans =
3.1416
--> pi=3.3
pi =
3.3000
--> pi
ans =
3.3000
--> pi(3.1416)
Error: index is out of bounds
--> pi=3.1416
pi =
3.1416
--> Sin(3.14)
Error: Undefined function or variable Sin
--> sin(3.14)
ans =
0.0016
--> %Sin is now used for as variable.
--> C=[1,2,3;4,5,6;7,8,9]
C =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
-->
-->
--> C
ans =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
--> A=0:0.5:10
A =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.5000 1.0000 1.5000 2.0000 2.5000 3.0000 3.5000 4.0000 4.5000 5.0000
Columns 12 to 21
5.5000 6.0000 6.5000 7.0000 7.5000 8.0000 8.5000 9.0000 9.5000 10.0000
--> A'
ans =
0
0.5000
1.0000
1.5000
2.0000
2.5000
3.0000
3.5000
4.0000
4.5000
5.0000
5.5000
6.0000
6.5000
7.0000
7.5000
8.0000
8.5000
9.0000
9.5000
10.0000
--> test1=[2345]
test1 =
2345
--> test1=[2,3,4,5]
test1 =
2 3 4 5
--> test2=test1'
test2 =
2
3
4
5
--> C=
Error: Unexpected input
C=
^
--> C
ans =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
--> C'
ans =
1 4 7
2 5 8
3 6 9
--> A=0:1:12
A =
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
--> B=e^A
Error: Power (^) operator can only be applied to scalar and square arguments.
--> B=sin(A)
B =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.8415 0.9093 0.1411 -0.7568 -0.9589 -0.2794 0.6570 0.9894 0.4121 -0.5440
Columns 12 to 13
-1.0000 -0.5366
--> B=
Error: Unexpected input
B=
^
--> B
ans =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.8415 0.9093 0.1411 -0.7568 -0.9589 -0.2794 0.6570 0.9894 0.4121 -0.5440
Columns 12 to 13
-1.0000 -0.5366
--> B'
ans =
0
0.8415
0.9093
0.1411
-0.7568
-0.9589
-0.2794
0.6570
0.9894
0.4121
-0.5440
-1.0000
-0.5366
--> N
Error: Undefined function or variable N
--> B
ans =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.8415 0.9093 0.1411 -0.7568 -0.9589 -0.2794 0.6570 0.9894 0.4121 -0.5440
Columns 12 to 13
-1.0000 -0.5366
--> b=B'
b =
0
0.8415
0.9093
0.1411
-0.7568
-0.9589
-0.2794
0.6570
0.9894
0.4121
-0.5440
-1.0000
-0.5366
--> B=b
B =
0
0.8415
0.9093
0.1411
-0.7568
-0.9589
-0.2794
0.6570
0.9894
0.4121
-0.5440
-1.0000
-0.5366
--> x=0:pi/10:2*pi
x =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.3142 0.6283 0.9425 1.2566 1.5708 1.8850 2.1991 2.5133 2.8274 3.1416
Columns 12 to 21
3.4558 3.7699 4.0841 4.3982 4.7124 5.0266 5.3407 5.6549 5.9690 6.2832
--> y=sin(x)
y =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.3090 0.5878 0.8090 0.9511 1.0000 0.9511 0.8090 0.5878 0.3090 -0.0000
Columns 12 to 21
-0.3090 -0.5878 -0.8090 -0.9511 -1.0000 -0.9511 -0.8090 -0.5878 -0.3090 0.0000
--> z=cos(x)
z =
Columns 1 to 11
1.0000 0.9511 0.8090 0.5878 0.3090 -0.0000 -0.3090 -0.5878 -0.8090 -0.9511 -1.0000
Columns 12 to 21
-0.9511 -0.8090 -0.5878 -0.3090 0.0000 0.3090 0.5878 0.8090 0.9511 1.0000
--> g=exp(x)
g =
Columns 1 to 11
1.0000 1.3691 1.8745 2.5663 3.5136 4.8105 6.5861 9.0171 12.3454 16.9021 23.1409
Columns 12 to 21
31.6824 43.3766 59.3873 81.3076 111.3190 152.4078 208.6629 285.6822 391.1300 535.4995
--> h=log10(x)
h =
Columns 1 to 11
-Inf -0.5028 -0.2018 -0.0257 0.0992 0.1961 0.2753 0.3422 0.4002 0.4514 0.4972
Columns 12 to 21
0.5385 0.5763 0.6111 0.6433 0.6732 0.7013 0.7276 0.7524 0.7759 0.7982
--> x=
Error: Unexpected input
x=
^
--> x
ans =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.3142 0.6283 0.9425 1.2566 1.5708 1.8850 2.1991 2.5133 2.8274 3.1416
Columns 12 to 21
3.4558 3.7699 4.0841 4.3982 4.7124 5.0266 5.3407 5.6549 5.9690 6.2832
--> BB=cos(x)-sin(x)
BB =
Columns 1 to 11
1.0000 0.6420 0.2212 -0.2212 -0.6420 -1.0000 -1.2601 -1.3968 -1.3968 -1.2601 -1.0000
Columns 12 to 21
-0.6420 -0.2212 0.2212 0.6421 1.0000 1.2601 1.3968 1.3968 1.2601 1.0000
--> CC=cos(x)*sin(x)
Error: Requested matrix multiplication requires arguments to be conformant.
--> CC
Error: Undefined function or variable CC
--> DD=cos(x).*sin(x)
DD =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.2939 0.4755 0.4755 0.2939 -0.0000 -0.2939 -0.4755 -0.4755 -0.2939 0.0000
Columns 12 to 21
0.2939 0.4755 0.4755 0.2939 -0.0000 -0.2939 -0.4755 -0.4755 -0.2939 0.0000
--> A=[1,2,3;4,5,6;7,8,9]
A =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
--> A
ans =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
--> A(1,1)
ans =
1
--> A(:,1)
ans =
1
4
7
--> A(1,:)
ans =
1 2 3
--> A(1:2,2:3)
ans =
2 3
5 6
--> B=A(:,1)
B =
1
4
7
--> C=A(1,:)
C =
1 2 3
--> C=3A(1,:)
Error: Unexpected input
C=3A(1,:)
^
--> C=3*A(1,:)
C =
3 6 9
--> D=A(1:2,2:3)
D =
2 3
5 6
--> degree=0:2*pi/100:2*pi
degree =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.0628 0.1257 0.1885 0.2513 0.3142 0.3770 0.4398 0.5027 0.5655 0.6283
Columns 12 to 22
0.6912 0.7540 0.8168 0.8796 0.9425 1.0053 1.0681 1.1310 1.1938 1.2566 1.3195
Columns 23 to 33
1.3823 1.4451 1.5080 1.5708 1.6336 1.6965 1.7593 1.8221 1.8850 1.9478 2.0106
Columns 34 to 44
2.0735 2.1363 2.1991 2.2620 2.3248 2.3876 2.4504 2.5133 2.5761 2.6389 2.7018
Columns 45 to 55
2.7646 2.8274 2.8903 2.9531 3.0159 3.0788 3.1416 3.2044 3.2673 3.3301 3.3929
Columns 56 to 66
3.4558 3.5186 3.5814 3.6443 3.7071 3.7699 3.8328 3.8956 3.9584 4.0212 4.0841
Columns 67 to 77
4.1469 4.2097 4.2726 4.3354 4.3982 4.4611 4.5239 4.5867 4.6496 4.7124 4.7752
Columns 78 to 88
4.8381 4.9009 4.9637 5.0266 5.0894 5.1522 5.2151 5.2779 5.3407 5.4036 5.4664
Columns 89 to 99
5.5292 5.5920 5.6549 5.7177 5.7805 5.8434 5.9062 5.9690 6.0319 6.0947 6.1575
Columns 100 to 101
6.2204 6.2832
--> output=sin(degree)
output =
Columns 1 to 11
0 0.0628 0.1253 0.1874 0.2487 0.3090 0.3681 0.4258 0.4818 0.5358 0.5878
Columns 12 to 22
0.6374 0.6845 0.7290 0.7705 0.8090 0.8443 0.8763 0.9048 0.9298 0.9511 0.9686
Columns 23 to 33
0.9823 0.9921 0.9980 1.0000 0.9980 0.9921 0.9823 0.9686 0.9511 0.9298 0.9048
Columns 34 to 44
0.8763 0.8443 0.8090 0.7705 0.7290 0.6845 0.6374 0.5878 0.5358 0.4817 0.4258
Columns 45 to 55
0.3681 0.3090 0.2487 0.1874 0.1253 0.0628 -0.0000 -0.0628 -0.1253 -0.1874 -0.2487
Columns 56 to 66
-0.3090 -0.3681 -0.4258 -0.4818 -0.5358 -0.5878 -0.6374 -0.6846 -0.7290 -0.7705 -0.8090
Columns 67 to 77
-0.8443 -0.8763 -0.9048 -0.9298 -0.9511 -0.9686 -0.9823 -0.9921 -0.9980 -1.0000 -0.9980
Columns 78 to 88
-0.9921 -0.9823 -0.9686 -0.9511 -0.9298 -0.9048 -0.8763 -0.8443 -0.8090 -0.7705 -0.7290
Columns 89 to 99
-0.6845 -0.6374 -0.5878 -0.5358 -0.4817 -0.4258 -0.3681 -0.3090 -0.2487 -0.1874 -0.1253
Columns 100 to 101
-0.0628 0.0000
--> plot(degree,output)
--> hold
--> hold off
--> plot(degree,output)
--> plot(degree,output)
--> plot(degree,cos(degree))
--> plot(degree,cos(degree))
--> plot(degree,cos(degree))
--> plot(degree,cos(degree))
--> plot(degree,output)
--> hold
--> plot(degree,cos(degree))
--> 1+3
ans =
4
--> hold
--> 3+4
ans =
7
--> plot(degree,output)
--> hold off
--> plot(degree,output)
--> hold
--> plot(degree,cos(degree))
--> 3+3
--> plot(degree,output)
--> plot(degree,cos(degree))
--> cosoutput=cos(degree)
cosoutput =
Columns 1 to 11
1.0000 0.9980 0.9921 0.9823 0.9686 0.9511 0.9298 0.9048 0.8763 0.8443 0.8090
Columns 12 to 22
0.7705 0.7290 0.6845 0.6374 0.5878 0.5358 0.4818 0.4258 0.3681 0.3090 0.2487
Columns 23 to 33
0.1874 0.1253 0.0628 -0.0000 -0.0628 -0.1253 -0.1874 -0.2487 -0.3090 -0.3681 -0.4258
Columns 34 to 44
-0.4818 -0.5358 -0.5878 -0.6374 -0.6846 -0.7290 -0.7705 -0.8090 -0.8443 -0.8763 -0.9048
Columns 45 to 55
-0.9298 -0.9511 -0.9686 -0.9823 -0.9921 -0.9980 -1.0000 -0.9980 -0.9921 -0.9823 -0.9686
Columns 56 to 66
-0.9511 -0.9298 -0.9048 -0.8763 -0.8443 -0.8090 -0.7705 -0.7290 -0.6845 -0.6374 -0.5878
Columns 67 to 77
-0.5358 -0.4817 -0.4258 -0.3681 -0.3090 -0.2487 -0.1874 -0.1253 -0.0628 0.0000 0.0628
Columns 78 to 88
0.1253 0.1874 0.2487 0.3090 0.3681 0.4258 0.4818 0.5358 0.5878 0.6374 0.6846
Columns 89 to 99
0.7290 0.7705 0.8090 0.8443 0.8763 0.9048 0.9298 0.9511 0.9686 0.9823 0.9921
Columns 100 to 101
0.9980 1.0000
--> plot(degree,output)
--> hold
--> plot(degree,cosoutput)
--> hold off
--> plot(degree,output,degree,cosoutput)
--> a=2
a =
2
--> square
Error: Undefined function or variable square
--> source 'C:/Users/ShengQuan/Desktop/square.m'
squared =
4
squareroot =
1.4142
--> a=2
a =
2
--> square
Error: Undefined function or variable square
--> square
Error: Undefined function or variable square
--> source 'C:/Users/ShengQuan/Desktop/square.m'
squared =
4
squareroot =
1.4142
--> source 'C:/Users/ShengQuan/Desktop/square.m'
squared =
4
squareroot =
1.4142
--> a=1-
Error: Unexpected input
a=1-
^
--> source 'C:/Users/ShengQuan/Desktop/square.m'
squared =
4
squareroot =
1.4142
--> a=10
a =
10
--> source 'C:/Users/ShengQuan/Desktop/square.m'
squared =
100
squareroot =
3.1623
--> source 'C:/Users/ShengQuan/Desktop/square.m'r
Error: source function takes exactly one argument - the filename of the script to execute
--> source 'C:/Users/ShengQuan/Desktop/square.m'r
Error: source function takes exactly one argument - the filename of the script to execute
--> source 'C:/Users/ShengQuan/Desktop/square.m'
squared =
100
squareroot =
3.1623
--> R=[50,40;40,60]
R =
50 40
40 60
--> V=[10;20]
V =
10
20
--> I=inv(R)*V
I =
-0.1429
0.4286
--> A=[30,-10;-10,15]
A =
30 -10
-10 15
--> C=[15;7]
C =
15
7
--> B=inv(A)*C
B =
0.8429
1.0286
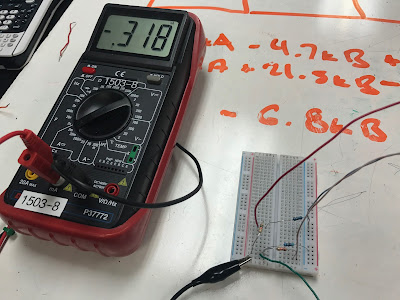
--> B(1)-B(2)
ans =
-0.1857
-->